hammertoe is a painful deformity wherein a toe bends unnaturally and becomes clawlike. This happens because the tendons of the toe contract abnormally, forcing the toe to bend downward and the middle joint of the toe to protrude upward. Although any toe may be affected, hammertoe usually affects the second toe. The toe assumes a clawlike position and cannot be straightened out. When someone with hammertoe wears shoes, the toe is constantly rubbed, so walking may become especially painful if a callus on the sole of the foot or a corn on the top of a toe develops.
Causes
The constant pressure a woman's foot receives in high-heeled shoes due to the force of gravity causes their feet to naturally slide down and press on the lowest point of the shoe so they are not able to receive enough space and stretch out. The result is an eventual distortion of the woman's toes. The deformity comes as a result of the shortening of muscles inside the toes because the toes become used to being in a bent position, prompting the muscles to fail to extend any further and become tightened and curbed. At first, toes may still be stretched out if poor footwear is not being worn, yet if the habit is persistent...the person's toes will eventually become used to the position they are constantly in and muscle fibers inside them will harden and refuse to stretch.
 Symptoms
SymptomsHere is a look at some of the symptoms hammertoe can cause. They include hammer-like or claw-like appearance of the Hammer toes toe. Pain when walking or moving the foot. Difficulty moving the toe. Corns may form on top of the toe. Callus may form on the sole of the foot. During the initial stages, you may be able to manually straighten your toe. This is called a flexible hammertoe. But as time passes, the toe will not move as easily and will continue to look like a hammer. Pressure and irritation over the joint can cause a blister to develop and become a corn over time. These corns have the potential to become infected and cause additional symptoms such as redness, bleeding, and difficulty wearing shoes and socks. Corns are the main cause of pain when hammertoes are developing.
Diagnosis
The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
If your hammertoe problem is diagnosed as flexible hammertoe, there are a number of nonsurgical treatments that may be able to straighten out your toe or toes and return them to their proper alignment. Padding and Taping. Your physician may pad the boney top-part of your hammertoe as a means of relieving pain, and may tape your toes as a way to change their position, correct the muscle imbalance and relieve the pressure that led to the hammertoe's development. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen can help deal with inflammation, swelling and pain caused by your hammertoe. Cortisone injections may be prescribed for the same purpose. If your hammertoe is a consequence of arthritis, your physician may prescribe medications for that.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative measures fail to provide relief, or if your hammertoe is in advanced stages with rigidity and a significant amount of pain, surgery may be required. Some patients also require surgery if they have open sores or wounds related to their hammertoe. For patients who also suffer from bunions, a combined procedure may be appropriate, addressing both conditions within the same surgery. Recovery time will vary from patient to patient, depending on the extent of the surgical repair and other conditions that may also be present.
 A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of your big toe. A bunion forms when your big toe pushes against your next toe, forcing the joint of your big toe to get bigger and stick out. The skin over the bunion might be red and sore. Wearing tight, narrow shoes might cause bunions or might make them worse. Bunions can also develop as a result of an inherited structural defect, stress on your foot or a medical condition, such as arthritis. Smaller bunions (bunionettes) also can develop on the joint of your little toes.
A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of your big toe. A bunion forms when your big toe pushes against your next toe, forcing the joint of your big toe to get bigger and stick out. The skin over the bunion might be red and sore. Wearing tight, narrow shoes might cause bunions or might make them worse. Bunions can also develop as a result of an inherited structural defect, stress on your foot or a medical condition, such as arthritis. Smaller bunions (bunionettes) also can develop on the joint of your little toes.

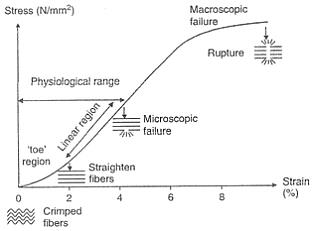
 The Achilles tendon attaches the calf muscles in the leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. An Achilles tendon rupture injury is when the tendon fibres tear, causing symptoms of pain and loss of function. A rupture can be either partial or complete and treatment may involve surgery. Achilles tendon rupture is most common in weekend athletes trying to train too hard and is least common in well-trained professional athletes. The injury is more common in men than in women and the frequency of rupture increases over the age of 30 years.
The Achilles tendon attaches the calf muscles in the leg to the heel bone. It is the largest yet most exposed tendon in the body. An Achilles tendon rupture injury is when the tendon fibres tear, causing symptoms of pain and loss of function. A rupture can be either partial or complete and treatment may involve surgery. Achilles tendon rupture is most common in weekend athletes trying to train too hard and is least common in well-trained professional athletes. The injury is more common in men than in women and the frequency of rupture increases over the age of 30 years.